In this blog, I am covering an approach to troubleshoot and find SQL queries when there is spike in Server CPU.
There would be scenario where the CPU on server was pegged at 100% for approx. 10 minutes yesterday at 4:00pm. In this case how do you find out what sql was running against the database at that particular time of yesterday?. If you able to find those queries were running at that specific time with other run time details, it helps to fine tune the system
Here is the solution
Many of you know that SQL server supports WMI alerts as part Alerting module. We are going to take advantage of WMI alert when there is CPU spike at the Windows server level.
With help of WMI alert, we can trigger a SQL agent job when CPU usage greater certain threshold. We have an custom stored proc (dbo.sp_Get_CPU_ConsumingSQL_Snapshot) which called in SQL agent job which does data collection of current running SQLs, text, query plan and number of thread etc along with CPUtime.
Sometimes there would be momentary spike for short time, those cases our WMI alert triggers which result into data collection. We mayn’t need to capture data during momentary spike.
Hence another logic added in our script to do cpu usage calculation with in SQL server again, and if it above threshold proceed to data collection.
There are functions in SQL server to find CPU activity. We are using in our script to calculate CPU.
The functions are
@@CPU_BUSY – Time that SQL Server has spent in active operation since its latest start.This value is cumulative for all CPUs.
@@IDLE – Returns the time that SQL Server has been idle since it was last started
Select @CPU_Busy = @@CPU_BUSY,
@Idle = @@IDLE
-- Delay for 1 second
WaitFor Delay '000:00:01'
-- Get current CPU counts and calculate % CPU utilization over the last 1 second
Set @CPUPercent = Cast(Round((@@CPU_BUSY - @CPU_Busy)/((@@IDLE - @Idle + @@CPU_BUSY - @CPU_Busy) * 1.0) * 100, 2) As decimal(5, 2))
@@CPU_BUSY , @@IDLE values are accurate up to only 49 days from last restart. It was mentioned in MSDN note.
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/t-sql/functions/idle-transact-sql?view=sql-server-2017
Hence, when you calculate CPU activity using @@CPU_BUSY and @@IDLE you will get arithmetic overflow error.
As a workaround, when its 49 days after system restart, we can retrieve CPU usage from ring buffers and proceed our logic. The ring buffers provides last 256 minutes for CPU utilization information. This logic mentioned many of articles
DECLARE @ts_now bigint = (SELECT cpu_ticks/(cpu_ticks/ms_ticks)FROM sys.dm_os_sys_info);
SELECT TOP(1) @CPUPercent=SQLProcessUtilization
FROM (
SELECT record.value('(./Record/@id)[1]', 'int') AS record_id,
record.value('(./Record/SchedulerMonitorEvent/SystemHealth/SystemIdle)[1]', 'int')
AS [SystemIdle],
record.value('(./Record/SchedulerMonitorEvent/SystemHealth/ProcessUtilization)[1]',
'int')
AS [SQLProcessUtilization], [timestamp]
FROM (
SELECT [timestamp], CONVERT(xml, record) AS [record]
FROM sys.dm_os_ring_buffers
WHERE ring_buffer_type = N'RING_BUFFER_SCHEDULER_MONITOR'
AND record LIKE N'%%') AS x
) AS y
ORDER BY record_id DESC OPTION (RECOMPILE)
So, next step is when CPU usage is above threshold, pull a data from DMVs currently running SQLs and their execution metrics.
SELECT TOP 25
qs.Session_Id as SessionID,
qs.CPU_Time as CPU_TimeMS,
DBName = db_name(qs.database_id),
ObjectName = object_name(qt.objectid, qs.database_id),
QueryText = SUBSTRING(qt.text, qs.statement_start_offset/2,
(Case When qs.statement_end_offset = -1
Then len(convert(nvarchar(max), qt.text)) * 2
Else qs.statement_end_offset
End - qs.statement_start_offset)/2),
qs.Reads,
qs.Logical_reads as LogicalReads,
qs.writes as Writes,
sp.login_time as LoginTime ,
qs.start_time as StartTime,
GETDATE() as CollectionTime,
(select max(isnull(ot.exec_context_id, 0))
From sys.dm_os_tasks ot where ot.session_id=qs.session_ID )+1
as NumberOfworkers
,@CPUPercent as CPUPercent
,qt.Text
,sp.host_name
,sp.program_name
,sp.login_name
,qs.last_wait_type
,qs.wait_type
,qs.wait_time
,qs.wait_resource
,qp.query_plan
FROM sys.dm_exec_requests qs
JOIN sys.dm_exec_sessions sp on qs.session_id = sp.session_id
Cross Apply sys.dm_exec_sql_text(qs.sql_handle) as qt
cross apply sys.dm_exec_query_plan (qs.plan_handle) as qp
WHERE qs.session_id <>@@SPID
ORDER BY qs.CPU_Time Desc, qs.logical_reads Desc;
The result data from above script to be stored in permanent table dbo.tblCPUconsumingQueries. Suggested to keep this table DBA specific database.
The data can be purged after certain day intervals. I usually purge older than a week data. This can be customized as per your requirement.
You can edit the CPU threshold value in in the WMI alert below highlighted EXEC msdb.dbo.sp_add_alert @name=@TEXT, @message_id=0, @severity=0, @enabled=1, @delay_between_responses=0, @include_event_description_in=0, @category_name=N'[Uncategorized]', @wmi_namespace=@wmi_namespace, @wmi_query=N'select * from __instancemodificationevent within 10 where targetinstance isa ''Win32_Processor'' and targetinstance.LoadPercentage > 65', @job_name=N'Infra_Capture_High_CPU_Queries' END
Here is the solution flow
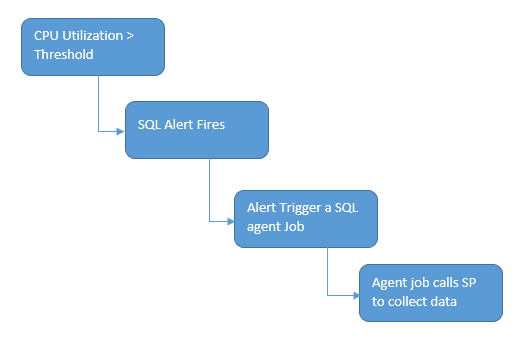
Objects Involved:
| Object Name | Object TYPE |
| sp_Get_CPU_ConsumingSQL_Snapshot | Stored Procedure |
| Infra_Capture_High_CPU_Queries | SQL agent job |
| Respond to High CPU | WMI Alert |
| tblCPUconsumingQueries | Permanent Table |
The complete setup script has provided here
In my script I created stored proc in master database. Feel free take the code and test and modify accordingly for your environment. if you change the database for stored procedure, you need to update in agent job as well as stored proc called in agent job
use master
GO
/Creating a stored proc to check CPU busy and capture currently running SQL to a table. Change the @Threshold value in Stored proc input parameter. Default @Threshold value set as 50 percent. I.e In the event of CPU alert fire, this stored proc again checks how busy CPU is and if > 65 then capture currently running SQL/
IF NOT EXISTS ( SELECT TOP 1 1 FROM sys.procedures where name = 'sp_Get_CPU_ConsumingSQL_Snapshot')
BEGIN
EXEC ( 'CREATE PROCEDURE sp_Get_CPU_ConsumingSQL_Snapshot as RETURN')
END
GO
ALTER PROCEDURE [dbo].[sp_Get_CPU_ConsumingSQL_Snapshot]
@Threshold int = 30
as
DECLARE @CPU_Busy INT,
@Idle INT,
@CPUPercent decimal(5, 2)
-- Get current CPU counts
--For systems which not restarted for long time
IF exists ( SELECT top 1 1 FROM sys.dm_os_sys_info where sqlserver_start_time < getdate()-49 ) BEGIN DECLARE @ts_now bigint = (SELECT cpu_ticks/(cpu_ticks/ms_ticks)FROM sys.dm_os_sys_info); SELECT TOP(1) @CPUPercent=SQLProcessUtilization FROM ( SELECT record.value('(./Record/@id)[1]', 'int') AS record_id, record.value('(./Record/SchedulerMonitorEvent/SystemHealth/SystemIdle)[1]', 'int') AS [SystemIdle], record.value('(./Record/SchedulerMonitorEvent/SystemHealth/ProcessUtilization)[1]', 'int') AS [SQLProcessUtilization], [timestamp] FROM ( SELECT [timestamp], CONVERT(xml, record) AS [record] FROM sys.dm_os_ring_buffers WHERE ring_buffer_type = N'RING_BUFFER_SCHEDULER_MONITOR' AND record LIKE N'%%') AS x
) AS y
ORDER BY record_id DESC OPTION (RECOMPILE)
END
ELSE
BEGIN
Select @CPU_Busy = @@CPU_BUSY,
@Idle = @@IDLE
-- Delay for 1 second
WaitFor Delay '000:00:01'
-- Get current CPU counts and calculate % CPU utilization over the last 1 second
Set @CPUPercent = Cast(Round((@@CPU_BUSY - @CPU_Busy)/((@@IDLE - @Idle + @@CPU_BUSY - @CPU_Busy) * 1.0) * 100, 2) As decimal(5, 2))
END
If @CPUPercent >= @Threshold
BEGIN
If object_id('dbo.tblCPUconsumingQueries') Is Null
BegiN
CREATE TABLE dbo.tblCPUconsumingQueries(
ID int identity(1, 1) not null primary key,
SessionID INT,
CPUTimeMs Bigint not null,
DBName sysname null,
ObjectName sysname null,
QueryText nvarchar(max) null,
Reads bigint null,
LogicalReads bigint null,
Writes bigint null,
LoginTime datetime,
StartTime datetime,
CollectionTime datetime,
NumberOfworkers int,
CPUPercent decimal(5, 2),
Text nvarchar(max),
HostName nvarchar(120),
ProgramName nvarchar(120),
LoginName nvarchar(128),
LastWaitType nvarchar(60),
WaitType nvarchar(60),
WaitTime int,
WaitResource nvarchar(256),
QueryPlan xml
)
END
---Capture Top 25 queries by CPU time
Insert Into dbo.tblCPUconsumingQueries
SELECT TOP 25
qs.Session_Id as SessionID,
qs.CPU_Time as CPU_TimeMS,
DBName = db_name(qs.database_id),
ObjectName = object_name(qt.objectid, qs.database_id),
QueryText = SUBSTRING(qt.text, qs.statement_start_offset/2,
(Case When qs.statement_end_offset = -1
Then len(convert(nvarchar(max), qt.text)) * 2
Else qs.statement_end_offset
End - qs.statement_start_offset)/2),
qs.Reads,
qs.Logical_reads as LogicalReads,
qs.writes as Writes,
sp.login_time as LoginTime ,
qs.start_time as StartTime,
GETDATE() as CollectionTime,
(select max(isnull(ot.exec_context_id, 0))
From sys.dm_os_tasks ot where ot.session_id=qs.session_ID )+1
as NumberOfworkers
,@CPUPercent as CPUPercent
,qt.Text
,sp.host_name
,sp.program_name
,sp.login_name
,qs.last_wait_type
,qs.wait_type
,qs.wait_time
,qs.wait_resource
,qp.query_plan
FROM sys.dm_exec_requests qs
JOIN sys.dm_exec_sessions sp on qs.session_id = sp.session_id
Cross Apply sys.dm_exec_sql_text(qs.sql_handle) as qt
cross apply sys.dm_exec_query_plan (qs.plan_handle) as qp
WHERE qs.session_id <>@@SPID
ORDER BY qs.CPU_Time Desc, qs.logical_reads Desc;
DELETE FROM tblCPUconsumingQueries
WHERE CollectionTime < GETDATE()-7
END
GO
GO
USE [msdb]
GO
IF NOT EXISTS (SELECT name FROM sysjobs WHERE name = 'Infra_Capture_High_CPU_Queries')
BEGIN
DECLARE @jobId BINARY(16)
DECLARE @schedule_id INT
EXEC msdb.dbo.sp_add_job @job_name=N'Infra_Capture_High_CPU_Queries',
@enabled=1,
@notify_level_eventlog=0,
@notify_level_email=3,
@notify_level_netsend=0,
@notify_level_page=0,
@delete_level=0,
@description=N'Fire on High CPU',
@category_name=N'[Uncategorized (Local)]',
@owner_login_name=N'sa',
@job_id = @jobId OUTPUT
EXEC msdb.dbo.sp_add_jobserver @job_name=N'Infra_Capture_High_CPU_Queries', @server_name = N'(local)'
END
IF NOT EXISTS (SELECT J.name,JS.step_name FROM sysjobs J INNER JOIN sysjobsteps JS ON J.job_id=JS.job_id WHERE J.name='Infra_Capture_High_CPU_Queries' AND JS.step_name='Infra_Capture_High_CPU_Queries')
BEGIN
EXEC msdb.dbo.sp_add_jobstep @job_name=N'Infra_Capture_High_CPU_Queries', @step_name=N'Infra_Capture_High_CPU_Queries',
@step_id=1,
@cmdexec_success_code=0,
@on_success_action=1,
@on_fail_action=2,
@retry_attempts=0,
@retry_interval=0,
@os_run_priority=0, @subsystem=N'TSQL',
@command=N'EXEC sp_Get_CPU_ConsumingSQL_Snapshot',
@database_name=N'master',
@flags=0
END
GO
USE [msdb]
GO
IF EXISTS(SELECT name FROM msdb..sysalerts WHERE name='Respond to High CPU')
BEGIN
EXEC dbo.sp_delete_alert
@name = N'Respond to High CPU'
END
DECLARE @wmi_namespace varchar(max)
DECLARE @instancename varchar(1000)
declare @server nvarchar(50)
DECLARE @productversion varchar(1000)
DECLARE @TEXT VARCHAR(1000)
SET @TEXT = 'Respond to High CPU'
SELECT @server=convert(nvarchar(50),(SERVERPROPERTY('ComputerNamePhysicalNetBIOS')))
SET @wmi_namespace=N'\'+@server+'\root\CIMV2'
/*"LoadPercentage" value defines threshold for CPU alert. Here hardcoded to report if cpu usage > 65 percent continously for 20 seocnds */
IF NOT EXISTS(SELECT name FROM msdb..sysalerts WHERE name=@TEXT)
BEGIN
EXEC msdb.dbo.sp_add_alert @name=@TEXT,
@message_id=0,
@severity=0,
@enabled=1,
@delay_between_responses=0,
@include_event_description_in=0,
@category_name=N'[Uncategorized]',
@wmi_namespace=@wmi_namespace,
@wmi_query=N'select * from __instancemodificationevent within 20 where targetinstance isa ''Win32_Processor'' and targetinstance.LoadPercentage > 65',
@job_name=N'Infra_Capture_High_CPU_Queries'
END
GO
Hi Maha,
It is good one. Will be very useful for many DBAs.
Thanks for sharing.
LikeLiked by 1 person
Hi Maha,
Good article, it’s looks like an AWR- repository which is available in oracle.we can check and retrieve past high cpu consumed queries for tune.
LikeLiked by 1 person
Nice information on CPU . Thanks a lot for providing good article about CPU ticks .
LikeLiked by 1 person
Thanks maha,
Very good one. Hoping to see many posts From you
LikeLiked by 1 person
Hi Maha,
It’s very useful information & Good effort. Thanks
LikeLiked by 1 person
Great Post Maha! Thanks for sharing.
LikeLiked by 1 person
Very good and useful. Hoping to see many posts..
LikeLiked by 1 person
Good Article on CPU Spikes. Thanks Maha..!
LikeLiked by 1 person